Topics To Be covered
- Position and Reference Point
- State of Motion (Rest and Motion)
- Types of motion
- Uniform motion and Nonuniform motion
- Physical quantity and system of units
- Distance and Displacement
- Speed and Velocity
- Acceleration and Retardation
- Graphical Representation of Motion a) Distance – Time graph b) Velocity – Time graph
- Equation of motion
- Derivation of equations of motion by Simple Algebraic Method
- Derivation of equations of Motion by Graphical Method
- Circular motion
Position:- the position of a body is defined as how far it is from a reference point and in what direction.

Reference Point and Reference Frame
To describe the position of an object, we need a reference point or origin. An object may seem to be moving to one observer and stationary to another.
In physics there are two state of motion
Rest (stationary)
Motion
Rest:- A body is said to be in state of rest when it’s position does not change with respect to a reference point and with respect to time.
Motion:- A body is said to be in motion or moving when its position changes continuously with respect to time in presence of reference point.
Types of motion
1. Random motion
2. Translation motion
a) Rectilinear motion or Linear Motion
b) Curvilinear motion or circular motion
3. Rotational motion
4. Vibration or oscillatory motion
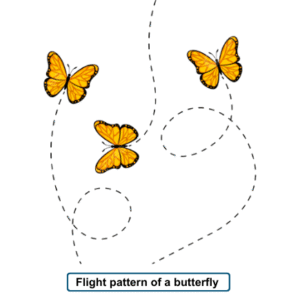
Random motion:- When the object moves in zigzag motion not move in straight line is called random motion
For example:- Motion of a butterfly, Motion of a particle
Translational motion:- The motion in which all the points of moving body moves uniformly in the same linear direction, without any rotation or change in orientation.
There are two types of translation motion
Rectilinear motion or linear motion
Curvilinear motion or circular motion
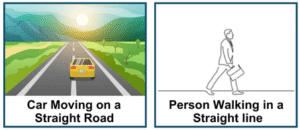
Rectilinear motion or linear motion:- When a body travels in the straight line then the body is said to be in a linear motion
For example:- A car driving on a long, straight road or a person walking in a straight line.
Curvilinear motion or circular motion:- If a body travels along a curved path than the body is said to be in circular motion .
For example:- A roller coaster ride where the track twists and turns, or a bicycle going around a circular path.

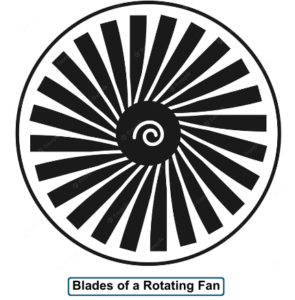
Rotational Motion:- When a body rotates about a fixed axis is called rotational motion
For example:- The blades of a rotating fan or a potter’s wheel. The object stays in the same place with respect to time, but different parts of it move at varying distances.
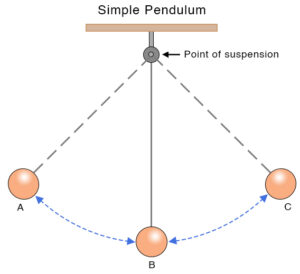
Vibration or Oscillatory motion :-
If a body shows to and fro movement then the body is said to be oscillatory motion for vibration motion
For example :- pendulum
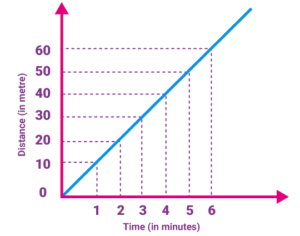
Unif0rm Motion And Non Uniform Motion :-
Uniform motion or uniform speed or constant speed
If an object covers equal distance in equal interval of time then it is speed is called uniform speed no matter how small these time intervals may be.
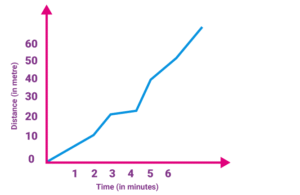
Non uniform motion or variable speed or non uniform speed
If an object covers unequal distance in equal interval of time then its speed is called non uniform speed.
Magnitude
Magnitude is the size or extent of a physical quantity. In physics, we have scalar and vector quantities.
Scalar quantity: It is the physical quantity having own magnitude but no direction.
Example: distance, speed, time, mass, temperature, area, volume
Vector quantity: It is the physical quantity that requires both magnitude and direction.
Example: displacement, velocity, weight, momentum, force, acceleration, etc.
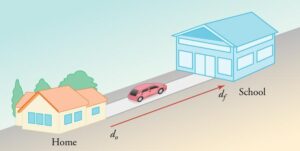
Distance and Displacement:-
Distance:- It is the complete length of the path by a moving body irrespective of the direction in which the body travels.
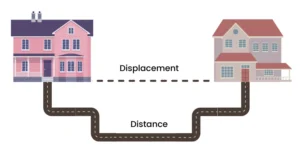
The distance between two points can have different value.
It is a scanner quantity.
Distance cannot be zero or negative.
Distance has only magnitude.
Distance has no specified direction.
Distance is denoted by “D”.
The unit of distance is meter “m”.
Distance is always greater than or equal to the displacement.
Displacement:- The shortest distance between the initial position and the final position of the body along with direction is called displacement
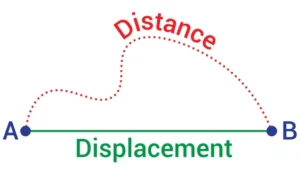
It is a vector quantity
It has magnitude as well as direction
Displacement of an object can be zero or negative
Displacement has specified direction
Displacement of a body between two points has unique value.
Displacement is less than or equal to distance.
Displacement can either be positive or negative or zero (when initial point and final point of motion are same)Example: circular motion.
Speed and Velocity
Speed:- The speed of a body gives us an idea how slow or fast that body is moving.
Or
The rate at which distance is covered is called speed.

SI unit of speed is meter per second (m/s)
Speed is a scalar quantity.
Speed has only magnitude.
* Speedometer is an instrument which tells about the speed of vehicle.
* Odometer is an instrument which tells about the distance covered by the body.
Types of speed
Average speed
Instantaneous Speed

