Matter in our surrounding
Topics To Be Covered
1. Matter ( Definition )
2. Types on the basis of physical and chemical properties
3. Brownian motion
4. Terminology
5. Classification of matter
6. Density
7. Diffusion
8. Scale of temperature
9. Melting and melting point
10. Boiling and boiling point
11. Sublimation and deposition
12. Latent heat and type
13. Specific heat
14. Effects of change in pressure
15. Relation between temperature and pressure
16. Evaporation ( factor affecting evaporation )
17. Plasma state of matter
18. Boss Einstein condensate
It is the study of physical world and natural draw.
There are three branches of science:-
1. PHYSICS :-
It is the study of physical phenom such as motion, force, energy, density. pressure, magnitude, electric current, there application and uses.
Father of physics :- sir laic newton.
CHEMISTRY :- It is the study of atoms, molecules, compounds, their structure and properties.
FATHER OF CHEMISTRY :- Antoine Lavoisier
BIOLOGY :-
It is the study of life.
FATHER OF BIOLOGY :- Aristotle
There are various branches of physics :–
1. Optics :- study of light
2. Acoustic :- study of sound
3. Mechanism :- study of motion , force , energy , in 2D and 3D plate.
4. Fluid mechanics :- study of fluids and its applications.
5. Electrocutes :- study of electrical equipment and semiconductor.
6. Electricals :- study of electric current
7. Magnetism :- study of magnet
There are 3 type of chemistry :-
Physical dentistry :-
It is the branch of chemistry in which we study about physical states and physics properties such as volume , density , temperature , heat , & moles .
Matter in our Surrounding :-
Matter :-
An those substances which having mass and occupies in called matter.
Matter are made up of tiny particles these particles are known as atom and molecules.
According to Indian philosopher matter is made up of a element.
There elements are :- Earth, Water, Fire, Sky, Air,
On modern day matter are classified on the basis of physical and chemical properties.
On the basic of physical properties matter are classified into three types :-
1. Solid
2. Liquid
3.Gas
On the Basics of chemical properties matter all classified as elements and mixture.
Brownian motion :-
Motion of particles within the matter is known as Brownian motion particles exhibit 3 types of motion.
Linear motion :-
Motion of particles on straight path.
Rotational motion :-
Motion of particles on their area.
Oscillatory motion :-
Eg :- To and two motion ( back and forth) most of particles.
To and two & up and down & back and forth & forward and backward
Brownian motion of particles was first line observed by Robert brown.
He observed motion of pollen grains in water.
Direction of Brownian motion is zig, zag or indeterminate.
Brownian motion can be observed in gases and liquid when a beam of sunlight enter a room we can see ting dust particles suspended in air which are ronin rapidly hence and there on a zig – zag path .
The existence of Brownian motion given us two concerns about the nature of matter
The metal is made up of tiny particles.
The particles are constantly movie.
Rigidity :-
it mean inflexible or unbending solid are hard and rigid due to best intermolecular space between atom .
Fluidity :-
Flowing nature of of matter is called fluidity.
Fluid shows fluidity nature material.
Fluid :-
The material which can flow easily.
Exp :- Liquid and gas
Fluidity nature of materials cause due to intermolecular between the particles.
Order of Fluidity :- Gaseous } liquid
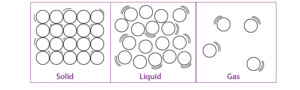
Classification of matter :-
Matter can be classified into three category :-
1. SOLID :-
The Matter which are hard and rigid called solid.
Properties of matter :-
I ) it has fixed shape and mix volume.
II ) I cannot be compressed due to least intermolecular shape .
III ) it has life density.
IV ) it do not fire their constancies.
V ) it do not flow.
2. Liquid :-
The matter which can flow and having unfixed shape fixed volume called liquid.
Properties :-
I ) it cannot be compressed.
II ) it has moderate densities .
III ) it do not fill their contains Completely.
IV ) it can flow ( operate on the surface )
3. Gas :-
The matter which have neither fixed shape and not fixed volume called gas.
Properties :-
I ) it can be compressed due to most intermolecular shape.
II ) it has least density.
III ) it can feel their contains.
IV ) it can flow.
Density :-
It is Mass per unit volume of metal.
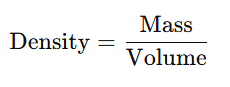
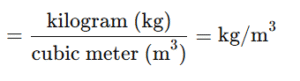
Diffusion :-
Intermixing of particles of Our substance into particles of another substance is called diffusion.
-Diffusion is fastest into gas and slowest in solid because intermolecular shape in gas is most and it intermolecular shape is solid and least.
Factors, Effecting, Diffusion :-
– Date of diffusion increases on increasing the temperature of diffusion substances because on increasing temperature kinetic energy of diffusing particles increase.
Exp :- Diffusion Gas
1 . The smell of food cooked in kitchen reaches to us even from considerable distance.
2 . The frequency of increase stick ( agarbatti ) spreads all around us due to diffusion of its smoke in the air.
3 . The smell of perfumes spiracles due to Diffusion of its vapor in air
Diffusion in Liquid :-
( Diffusion in Liquid is slower then diffusion in Gas )
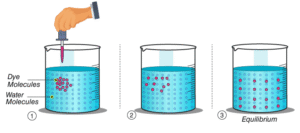
I ) spreading of purple colour of potassium permanganate { km2 O4} into what are due it’s Diffusion of particles of potassium permanganate into water.
II ) spreading of blue colour of copper sulphate ( C43O4 ) into water due to Diffusion of particles of copper sulphate into water.
III ) Spreading of ink { silver nitrate ( AgNO3) }
Into water due to diffusion of part of into water
Diffusion in Solid :-
– Diffusion in solid is slowest process
– Diffusion of our types of solid particles into another types of solid particles takes many days and many years.
I ) intermixing of choke particles into blackboard { it takes 15 days and more }
II ) intermixing of iron particles into copper particles { it takes 100 years and more }
Order of diffusion > Gas > Liquid > Solid
Unit of temperature :-
Temperature :-
It expiress the hottest and coldest of an object.
SI unit of temperature = Kelvin

There are five other unit of temperature :-
1. Kalvin scale = lord William Thomson Kelvin
2. Degree Celsius scale = Anders Celsius
3. Fahrenheit scale= William John Macqueen Rankine
4. Reaumur scale = R.A Reaumur
5. Rankine scale = William John Macqueen Rankine
– The flow of heat from our body to another body is due to temperature difference.
– Hit flop from light temperature to low temperature.
Thermometer :-
It is a device used to measure the temperature of body. It’s given by a Galileo.
Conversation of temperature from the scale to another scale .
Interconversion of state of matter :-
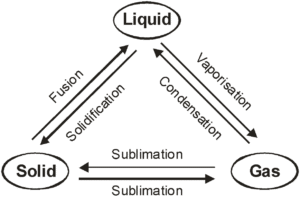
A) On the basis of temperature :-
1. Fusion
2. Melting point
3. Vaporization
4. Boiling point
5. Condensation
6. Sublimation
B) On the basis of pressure :-
1) Fusion ( Melting ) :-
It is the process of melting or in this process solid change into Liquid on heating.
2) Melting Point :-
The temperature at which a solid start to melt to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called melting point.
S.
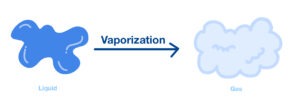
3) Vaporization :-
It is the process in which liquid converted into gas on heating called Vaporization
4) Boiling Point :-
The temperature at which liquid start boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as it’s Boiling point .
Boiling point of water is 100 ° C .
5) Condensation :-
It is the process in which gas changes into Liquid state or solid state on cooling are known as Condensation.
6) sublimation :-
The process in which solid directly converted into gas or heating
Condensation
Solid <———————
——————
iOTA CLASSES has been working for the last 6 years at youtube ( online mode) but from last year ( 2024) we are running both online and offline,
With the cooperation of students , parents , our colleagues and team, we have gained satisfactory results,
And working more enthusiastically for the better aspirations. image of 2024 class 10th result [CBSE and BSEB( ENG. Med)]
