Gravitation Class 9
Topics to be covered:
- Gravity and Gravitation
- Universal laws of Gravitation
- Application of universal laws of Gravitation
- Numerical
- Contribution of Scientist
- Kepler’s law of Planetary motion
- Freefall ⇒ Numerical
- Acceleration due to Gravity (g)
- Variation of acceleration due to Gravity
- Equation of motion for free fall bodies
- Mass and Weight
- Thrust and Pressure
- Buoyancy
- Archimedes Principles
- Relative density
Gravitational Force →
Newton said that every object in this universe pulls every other object with a certain force.
Or,
Gravitational force is an attractive force that every object in this universe exert on every other object in the universe.
Gravity →
The force with which the earth pulls the object towards its is called force of gravity or gravity.
→ The average gravitational force of earth is 9.8 m/sec²
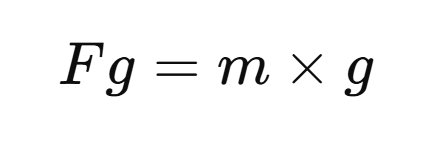
Universal law of Gravitation
→ The universal law of Gravitation is also known as Newtons law of gravitation.
→ It states that every body in this universe attracts every other body with a force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
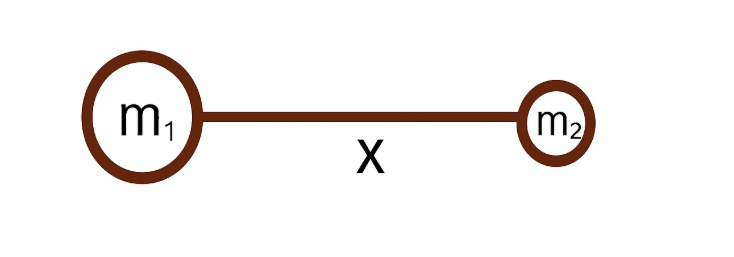
(i) The force between two bodies is directly proportional to the product of their masses.
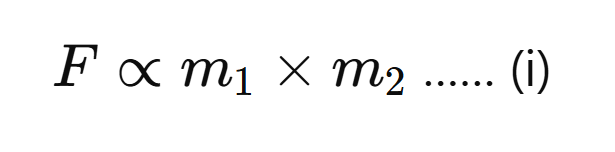
(ii) The force between two bodies is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.

• From equation (i) and (ii),
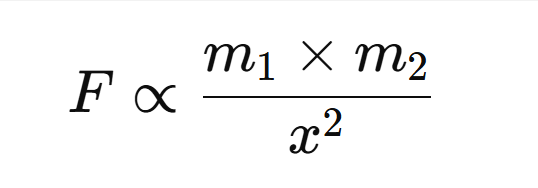
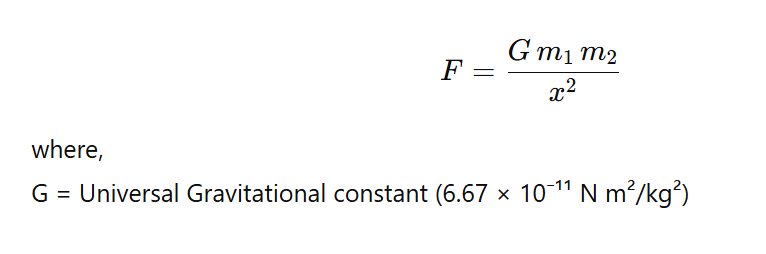
In others words
➩ Gravitational force is a non-contact force.
➩ It is always attractive in nature. (Gurutvaakarshan Shakti)
➩ It depends directly on the masses and inversely on the square of the distance.
➩ Inverse square law applicable to charges, masses, magnetic poles.
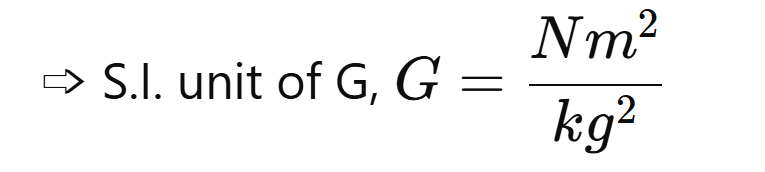
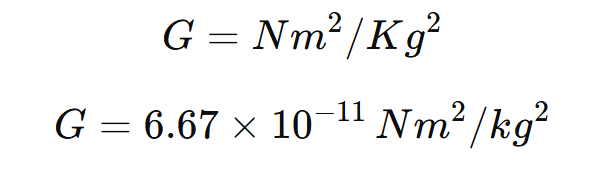
Application of Universal laws of Gravitation
- The universal law of gravitation helps in determining the accurate mass of the sun, the earth, the moon, etc.
- It helps to calculate the force or pull of gravity of the planet in the universe.
- It helps in discovery of new star and planet.
- It helps to the rotation of the earth around the sun.
- It helps to the rotation of the moon around the earth.
- The formation of tides in the ocean is due to the force of attraction between the moon and the ocean water.
- It helps in the accurate prediction of the solar and lunar eclipse.
Contribution of Scientists
➩ In 140 AD Ptolemy gave a theory which was geocentric theory. He told us that earth is in center and the rest planets even sun revolves around the earth.
➩ In 1543 Nicolaus Copernicus gave another theory which was heliocentric theory. He told us that it is the sun which is in the center and the rest planets revolve around the sun.
➩ In 1588 Tycho-Brahe gave another theory which was Tychonic system. According to this theory moon was in center and the rest planets revolve around the moon.
➩ In 1609 Galileo Galilei came with telescope and he supported and he supported Nicolaus Copernic’s theory of heliocentric theory.
Kepler’s law of Planetary motion
➩ He stated three laws which govern the motion of planets around the sun. These are known as Kepler’s laws of planetary motion.
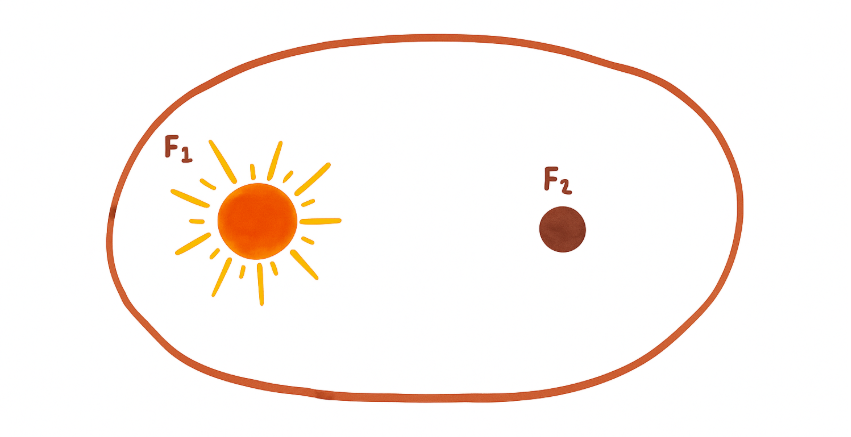
1. Kepler’s 1st law of Motion.
The planets moves in elliptical orbits around the sun, with the sun at one of the two foci of the elliptical orbit.
2. Kepler’s 2nd law of Motion.
➩ Each planets revolves around the sun in such a way that the line joining the plant to the sun sweeps over equal area in equal interval of time.

➩ A planet moves faster when it is closer to the sun and moves slowly when it is farther from the sun.
3. Kepler’s 3rd law of Motion.
➩ The cube of the mean distance of a planet from the sun is directly proportional to the square of the time, it takes to move around the sun

• How did Newton guess the inverse square rule
→ The statement met by Newton in his universal law of gravitation that the force between two bodies is inversely proportional to the square of distance between them is called inverse square rule.
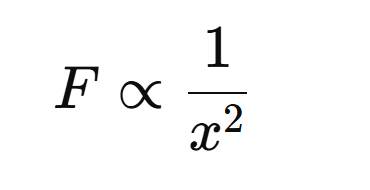
• Let m be the mass of the planet which is moving with the velocity v around the sun in a circular orbit of radius x. Therefore a centripetal force (F) on the orbiting planet is given.
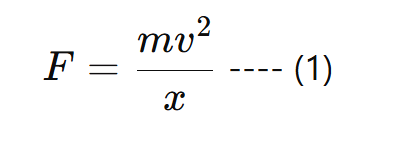
Let planet takes T time to complete one regulation around the sun then its velocity will be
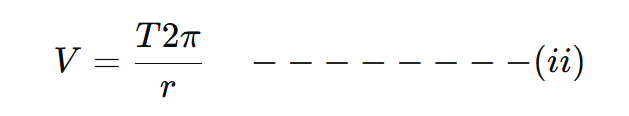
On putting the value of v in equation (i) we get
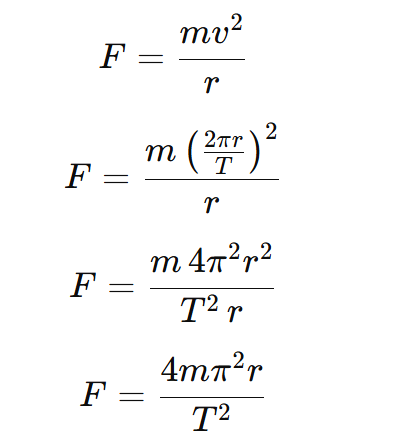
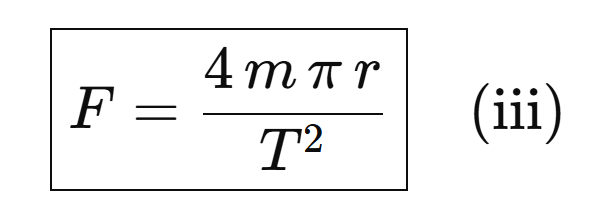
From Kepler’s 3rd law of Planetary motion:
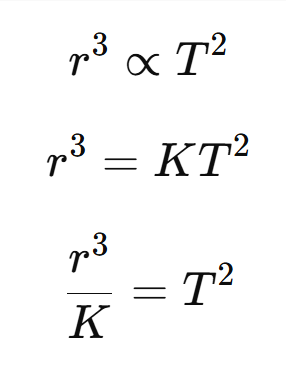
On putting the value of equation (iii)
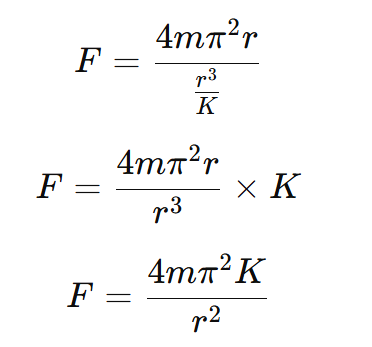
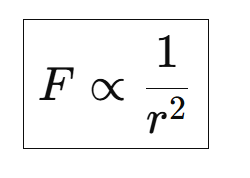
• Free Fall →
Free Fall is the downward motion under the influence of gravity.
↪ In other word, When the only force acting on an object is gravity the object is said to be free fall.
↪ In a vacuum (no air) all objects in free fall accelerate at the same rate, regardless of mass.
Question:
A body is dropped from a building of height 120m. Find its total time of fall and the velocity with which it strikes the ground.
Answer:
Given,
u = 0 m/sec²
t = ?
h = -120 m
g = -10 m/sec²
v = ?
To find: total time and velocity
Solution:
v² = u² + 2gh
v² = 0 + 2 × -10 × -120
v² = 0 + 2400
v² = 2400
v = ±√2400 = -20√6 m/s
h = ut + ½ gt²
-120 = 0 × t + ½ × (-10)(t²)
+120 = +5t²
t² = 120/5
t² = 24
t = √24
t = 2√6 sec.
Acceleration due to gravity (g)
➩ The unform acceleration product in a freely falling body due to gravitational force of the earth.
➩ S.I unit is m/sec2
➩ Denoted by small (g).
➩ It has both magnitude and direction.
➩ (g) does not depends on the mass of falling object or smaller mases.
Calculation of acceleration due to gravity (g)
➩ Force exerted by earth on the body.
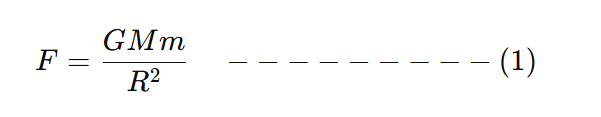
Now, force by earth produces acceleration in the stone due to which stone moves downward.
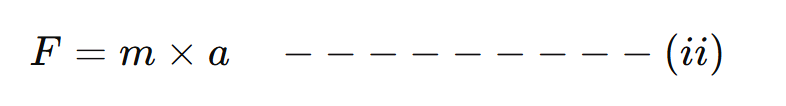
From equation (i) and (ii) we get
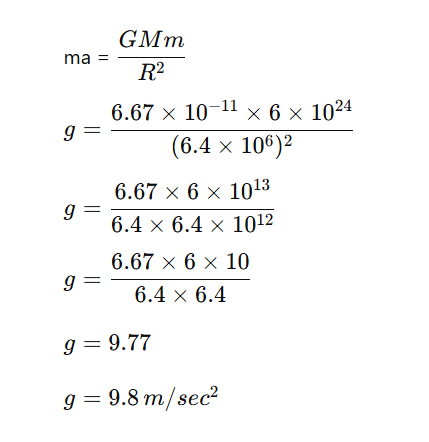
Why gravity (g) does not depends on mass of any body?
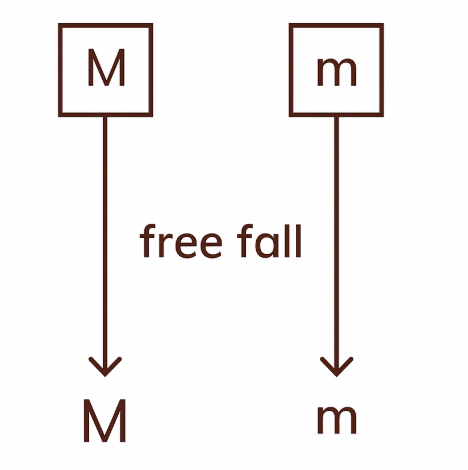
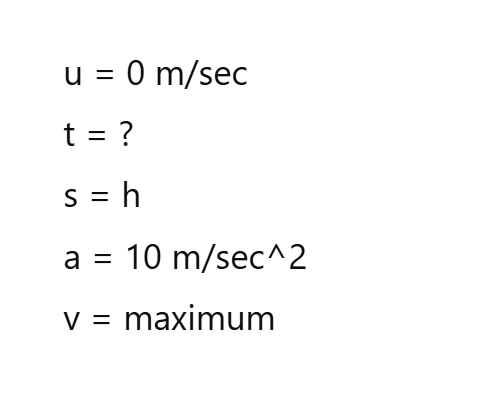
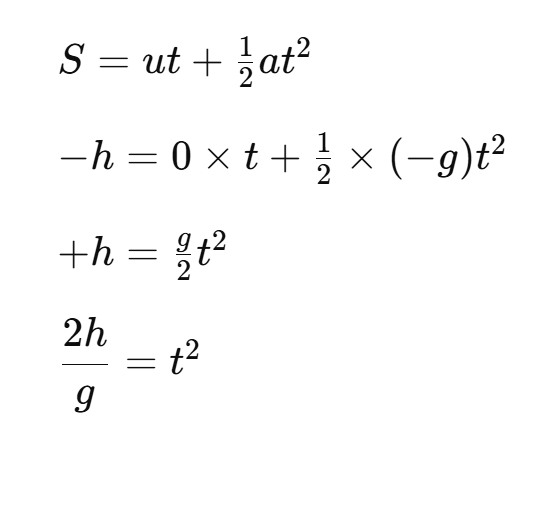
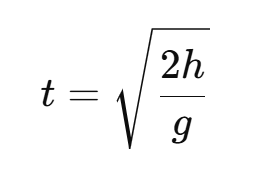
(time of fall does not depends on masses of the body)
Question:
Find the acceleration due to gravity of a planet mass half as that of earth and radius twice as that of the earth.
Answer, Given

Home – View
Official Website- Physics Walla
iOTA CLASSES has been working for the last 6 years at youtube ( online mode) but from last year ( 2024) we are running both online and offline,
With the cooperation of students , parents , our colleagues and team, we have gained satisfactory results,
And working more enthusiastically for the better aspirations. image of 2024 class 10th result [CBSE and BSEB( ENG. Med)]




