Light Class 8
Light
Optics :- study of light is called optics. Light :- it is a form of energy which gives us sensation to see any objects. • We see any object due to reflection of light. Source Of Light :- A source of light is an object from which light is given out. Source of light are natural and many others are man made.
Types Of Source of light i) Self luminous ii) Non luminous or Illuminated i) Self luminous:- It is a source of light which has the ability to produce the light on its own. Ex:- Sun, Stars, Bulb, Candle, firefly etc.
Natural Sources of Light
Natural sources of light are those that emit light on their own and are not created or controlled by humans. These sources occur in nature and produce light through natural processes such as nuclear reactions, chemical reactions, or heat.
Ex:- The Sun, Stars, Lightning, Volcanic lava, Firefly etc.
Artificial Sources of Light
Artificial sources of light are man-made objects that produce light using electricity, chemicals, or other technological means. These sources do not occur naturally and are created by humans to provide light, especially when natural light is unavailable.
Examples of Artificial Sources of Light:
Electric Bulbs, Tube Lights, LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes), Lasers, Candle and Oil Lamps, Television and Phone Screens etc.
ii) Non luminous or Illuminated:- A non luminous source of light is that which does note produce light its own. Ex:- Moon, Chair, bench, planets etc.
There are various application of light :-
1. Reflection of light 2. Refraction of light 3. Dispersion of light 4. Scattering of light
On the basis of light these are 3 types of material or surface .
1. Opaque surface :- The surface through which ray of light can’t pass , called opaque surface . Ex :- wall, wood , paper , plastic etc. 2. Transparent surface:- The surface through which ray of light can pass easily called transparent surface . Ex :- glass, water, diamond etc. 3. Translucent surface :- The surface through which practical ray of light can pass but rest reflected in the same medium called translucent surface. Ex :- oiled paper , frosted glass, dusty water
Reflection of light :-
When ray of light incidence on an opaque surface then the surface bounce back the ray of light in the same medium, this phenomena of light is known as reflection of Light  The ray of light which falls on the plane surface is called incident ray The ray of light which is sent back by the plane surface is reflected rays The perpendicular which is drawn on the surface is called normal. The point at which the incident ray fall on the surface is called point of incidence.
The ray of light which falls on the plane surface is called incident ray The ray of light which is sent back by the plane surface is reflected rays The perpendicular which is drawn on the surface is called normal. The point at which the incident ray fall on the surface is called point of incidence.
There are two laws of reflection:
1st laws :- According to first law of reflection of light angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection. “i” is the angle of incidence “r” is the angle of reflection ∠i = ∠r  2nd laws :- According to second law of reflection of light Incident ray, reflected ray & normal lie in the same plane at same point of incident. Note :- If the light ray falls normally or perpendicular on the surface then it will be reflected back along the same path. ∠i = ∠r = 0
2nd laws :- According to second law of reflection of light Incident ray, reflected ray & normal lie in the same plane at same point of incident. Note :- If the light ray falls normally or perpendicular on the surface then it will be reflected back along the same path. ∠i = ∠r = 0
Types of Reflection
(1) Regular Reflection:
When ray of light incident on smooth or polished surface then regular reflection takes place. All reflected rays will be parallel to each other if incident rays are parallelly incident on the surface. Intensity of image will be as usual. Single intensified image is formed. 
1. Irregular Reflection
When ray of light incident on rough surface then irregular reflection takes place. • All reflected rays will not be parallel to each other if incident rays are parallelly incident on the surface. • Intensity of image will be dull. • More than one image is formed.

Reflection on Plane Surface
Plane Mirror: It is a reflecting object whose one face is reflecting and another face is polished.

IMAGE
When two or more reflected rays either meet or appear to meet, then image is formed.
There are two types of images:
Real Image
Virtual Image
Real Image
Real image is when two or more reflected rays actually meet after reflection, then real image is formed. Real image can be obtained on the screen and it can be touched. Real image can be formed by concave mirror and convex lens.
(2) Virtual Image (Imaginary)
When two or more reflected rays appear to meet after reflection, then virtual image is formed.
Examples
(i) Plane mirror
(ii) Convex lens
(iii) Concave lens
(iv) Concave mirror
(v) Convex mirror
Image Formation in a Plane Mirror
- Image formed by mirror is virtual and erect.
In plane mirror, the distance of object in front of the mirror () is always equal to distance of image formed by the mirror ():
In plane mirror, height of object is equal to height of image. HO=HI
In plane mirror, left part of object appears right and right part of object appears left.
This phenomenon in plane mirror is called lateral inversion.

Multiple Reflection in plane Mirror
When two plane mirrors are inclined at angle θ then more reflection on the surface. This phenomena is known as multiple Reflection It causes formation of more then one image  1) If N is odd, then no. of image = N Here L₁ L₂ & L₃ are image formed by plane mirror.
1) If N is odd, then no. of image = N Here L₁ L₂ & L₃ are image formed by plane mirror. 
Note:-
• Focus of plane mirror is at infinite. • Focal length of plane mirror is infinite. • Magnification of plane mirror is 1. • Power of plane mirror is 0.
Uses of plane mirror
- Face mirror:- Plane mirrors are used to see our face
- Solar cooker
- The plane mirror are fitted on the inside wall of certain shops to make them look bigger.
- Plane mirrors are used in making Periscope
The human eye:-

• The human eye is one of the valuable and sensitive sense organ in the human body.
⇒ It enables us to see the wonderful world and colours around us.
Parts of eye
i) Cornea
ii) Pupil
iii) Iris
(iv) Eye Lens
(v) Retina
(vi) Optic nerves
(vii) Ciliary muscle
(viii) Sclera
(ix) Blind spot
(X) Aqueous humors
(xi) Vitreous humors
i) Cornea :-
It is the outermost parts of eye which prevent the eyeball from UV rays and maintain the shape and size of the Eyeball.
ii) Pupils :-
It is a round blackspot in front of Eye it regulates the amount of light entering the eye in case of deem light pupils expands to allow more light to enter eyes . • In case of strong light pupil contracts allowing less light to enter.
iii) Iris
It is made up of muscles. It control the size, of pupils. Its colour depends on melanin (pigment).
iv)Eye Lens :-
Lenses lie just behind the pupils. Lenses become thin or increases the focal length this enable us to see the distant object clearly to focus of nearer object lens become thick to decrease its focal length This process is known as power of accumulation. • The eye lens is lens made of soft and flexible proteins, Note – The minimum distance of clear vision is 25 cm. below this distance we can’t see things clearly without stress in Eye. ⇒ far point of vision for normal eye is infinity
v) Retina :-
Retina is a bow like screen or camera film. It is full of light and colour sensitive cells . This cells upon receiving image sends electrical signal to the brain which process these information to make a mental image of what we see.
The photo receptor cells in the eye are of two types
1) Rod cells 2) Cone cells
The rod cells sensitive dim light white cone cells are sensitive to bright light and colour.
vi) Optic nerve :-
It is transmit visual information from retina to brain.
vii) Ciliary Muscle :-
The ciliary muscle is located behind the iris. it controls the movements of eye lens through suspensory ligaments.
viii) sclera:-
It is an opaque , fibrous , protective outer layer of an eyes containing collagen and elastic fiber. • It is also known as white part of the eye.
ix) Blind spot :-
It is a spot between retina at the intersection of optics nerves where no cones and rods are present. • Due to which no image is formed at blind spot .
x) Aqueous Humor:-
Between the cornea and eye lens . It has a space filled with a transparent liquid called the aqueous humor which helps the refracted light to be focus on retina. • It also maintains intraocular pressure.
xi) Vitreous Humor
The space between the eye lens and retina is filled with another liquid called the Vitreous humor.
Power of accommodation :-
An eye can focus the image of the distance object as well as the near by objects on its retina by changing the focus length or converging power of its lens .
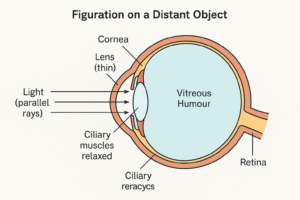
Fig :- An eye focused on near by object.
Formation of an image :-
• An image is formed on the retina by successive refraction at the cornea , the aqueous humor, lens and vitreous humor. • It is real diminished and inverted in nature. • The light sensitive cells of retina get activated upon illumination and generate electrical signal electrical impulses. • These signals are then send to the brain by the optic nerves . • The brain interpret these signals and finally process the information so that we receive objects as they are .
Defects of vision and these correction:-
I) Cataracts :-
In old age the cornea becomes cloudy this reduce the vision generally in the old age . • It can be cured by eye surgery. • Sometimes artificial lens is also transplant during cataract surgery this is called intraocular lens transplantation ( IOLT )
II) Myopia :-
Myopia is also known as near sightedness or short sightedness • A person with myopia can see near by object clearly but can’t see distant object clearly. • In myopic eye the image of distance objects form before the retina and not at the retina itself.
This effect may arise due to :-
i) Excessive curvature of the eye lens ii) Elongation of the Eyeball. Correction of myopic eye 
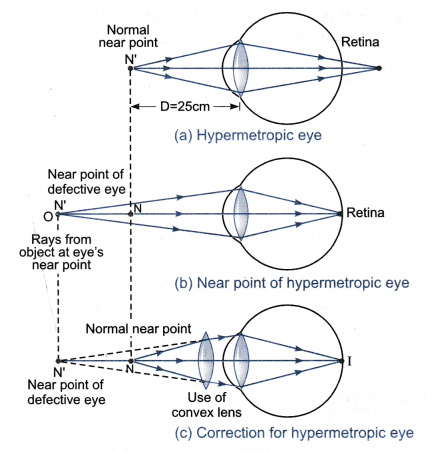
III) Hypermetropia
( Long sightedness or far sightedness ) • A person with Hypermetropia can see distant objects clearly but can’t see near by objects distantly. • The near point for the person is farther away from the normal near point 25 cm. • The light ray from a near by objects are focused at a point behind the retina.
The defect arise either because:-
i) the focal of the eye lens is too long.
ii) the Eyeball has become too small.
IV) Presbyopia :-
• A person who can’t see farther object as well as near by objects. • The power of accommodation of the eye usually decreases with ageing. • For most people the near point generally reduce away. • They find it difficult to see near by object comfortably and distinctly without corrective eyes ( glasses ) this defect is called press Byopia . • It arises due to gradual weaking of the Calgary muscle and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens .
Correction of pres Byopia :-
I ) By focal lens – sometimes a person may suffer from both myopia and Hypermetropia such people often require by -focal lens. – The upper portion consisting of a concave lens it fascinated distance vision – The lower part is concave lens , it facilitates near vision 
iOTA CLASSES has been working for the last 6 years at youtube ( online mode) but from last year ( 2024) we are running both online and offline,
With the cooperation of students , parents , our colleagues and team, we have gained satisfactory results,
And working more enthusiastically for the better aspirations. image of 2024 class 10th result [CBSE and BSEB( ENG. Med)]


