Reflection of Light Class 10th
TOPICS TO BE COVERED
- Introduction of Light
- Source of Light
- Nature of Light
- Important term related to light
- Reflection of Light
- Laws of reflection for plane mirror
- Types of Reflection
- Image and their types
- Image formation in a plane mirror
- Multiple reflection in a plane mirror
- Difference between real and virtual image
- Uses of plane mirror
- Spherical Mirror
- Terms Related to Spherical mirror
- Rules for making ray diagram for concave mirror
- Image formation in concave mirror in different position
- Uses of concave mirror
- Rules for making ray diagram for convex mirror
- Image formation in convex mirror in different position
- Uses of convex mirror
- Sign convention of Spherical mirror
- Mirror Formula
- Magnification
Light
Optics :- study of light is called optics.
Light :- it is a form of energy which gives us sensation to see any objects.
• We see any object due to reflection of light.
Source Of Light :- A source of light is an object from which light is given out.
Source of light are natural and many others are man made.
Types Of Source of light
i) Self luminous
ii) Non luminous or Illuminated
i) Self luminous:- It is a source of light which has the ability to produce the light on its own.
Ex:- Sun, Stars, Bulb, Candle, firefly etc.
Natural Sources of Light
Natural sources of light are those that emit light on their own and are not created or controlled by humans. These sources occur in nature and produce light through natural processes such as nuclear reactions, chemical reactions, or heat.
Ex:- The Sun, Stars, Lightning, Volcanic lava, Firefly etc.
Artificial Sources of Light
Artificial sources of light are man-made objects that produce light using electricity, chemicals, or other technological means. These sources do not occur naturally and are created by humans to provide light, especially when natural light is unavailable.
Examples of Artificial Sources of Light:
Electric Bulbs, Tube Lights, LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes), Lasers, Candle and Oil Lamps, Television and Phone Screens etc.
ii) Non luminous or Illuminated:- A non luminous source of light is that which does note produce light its own.
Ex:- Moon, Chair, bench, planets etc.
There are various application of light :-
1. Reflection of light
2. Refraction of light
3. Dispersion of light
4. Scattering of light
Nature Of Light:-
Different theories regarding light :-
1. Newton’s Corpuscular theory in 1675 :- It was given by sir Isaac Newton, According to him,
i) Light is emitted from luminous body in the form of tiny particles called corpuscular.
ii) This corpuscles moves in a straight line.
iii) Velocity of light in the denser medium is greater than the velocity in rare medium.
iv) Due to different size of corpuscles they produce different colour.
v) It helps to explain the phenomena of reflection, refraction and propagation of light.
2. Wave Theory Of Light in 1676:-
It was given by Huygens, According to him
i) Light travels in the form of wave.
ii) Light waves require medium for propagation.
iii) Velocity of light in the denser medium is less than the velocity in rare medium.
iv) He failed to explain the phenomena of reflection, refraction and propagation of light but he succeed to explain the phenomena of interference, diffraction and Polarization of light.
3. Electromagnetic Theory Of Light in 1873 by James Clerks Maxwell :-
According to James Clerks Maxwell,
i) Light is an electromagnetic in nature.
ii) Light wave does not require medium for propagation.
iii) Both of these fields are perpendicular to each other and also perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
iv) Light consist electric and magnetic field.
Conclusion :- He explained transverse nature of light.
4. Quantum Theory Of Light in 1905 by Max Plank :-
According to him,
i) Light is emitted in the form of energy packet or bundles called quanta or photon.
ii) The energy of these photon is directly proportional to the frequency of vibration.

Speed of light in vacuum :-
Speed of electromagnetic transverse wave = 3 × 10⁸ m/s.
Conclusion:- Nature Of Light
Light is not just a wave or a particle — it has a dual nature.
Modern physics accepts that light (and all quantum particles) have wave-particle duality, meaning they can behave like both depending on how we observe them.
Question :- Explain the dual nature of light.
Material wave Non material wave

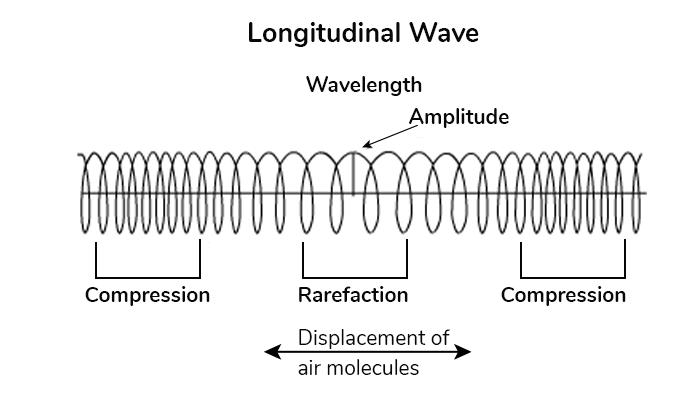
1. Longitudinal wave :-
It is the part of material wave .
★ Direction :- Back of forth
Ex :- Sound
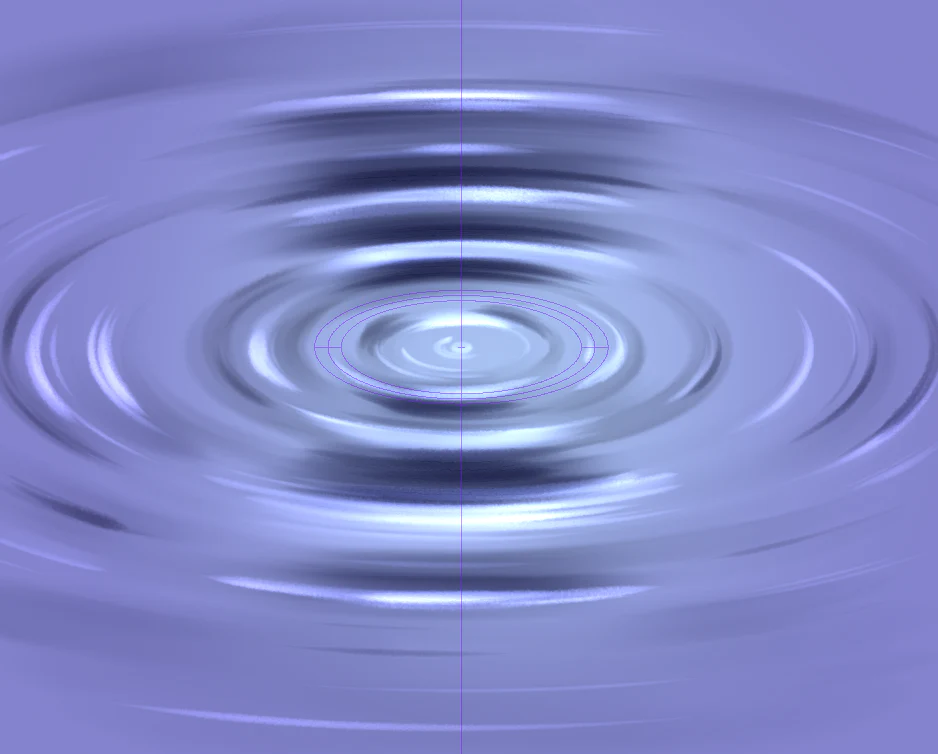
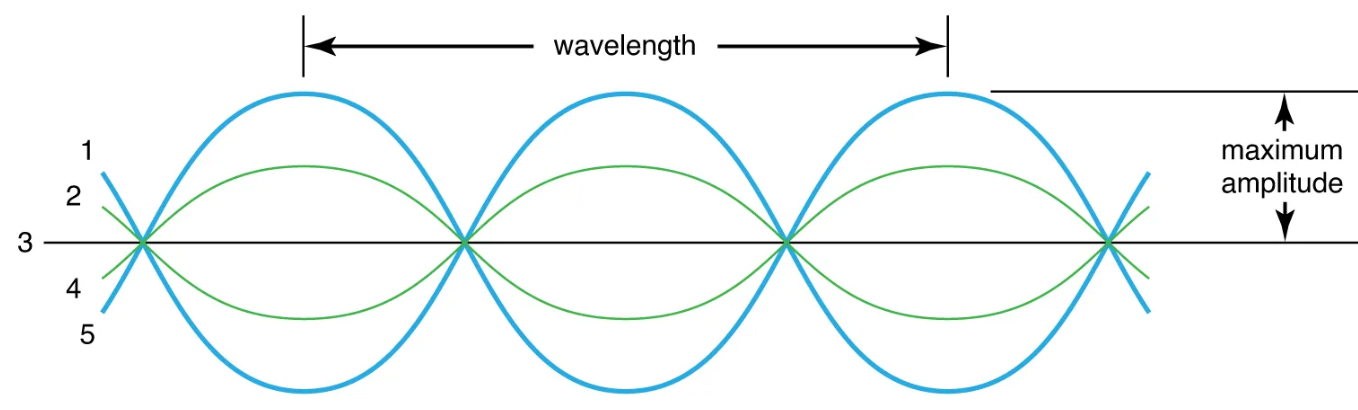
2. Transverse wave :-
It is a part of material wave .
★ Its direction is up and down .
Ex- ripples of water

★Frequency of wave S.I unit is Hz ( hertz)
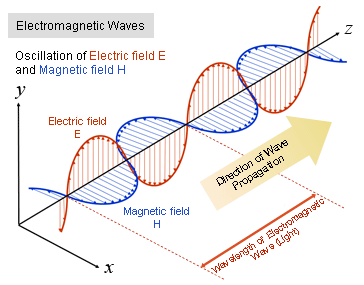
★ According to Maxwell. Light is an electromagnetic transverse wave
★ If electric field oscillates on y axis & magnetic field oscillates on x axis then a new wave electromagnetic wave oscillates along perpendicular to both electric & magnetic field is along Z— Axis, whole speed is 3×10 m/s.
On the basis of light these are 3 types of material or surface .
1. Opaque surface :-
The surface through which ray of light can’t pass , called opaque surface .
Ex :- wall, wood , paper , plastic etc.
2. Transparent surface:-
The surface through which ray of light can pass easily called transparent surface .
Ex :- class, water, diamond etc.
3. Translucent surface :-
The surface through which practical ray of light can pass but rest reflected in the same medium called translucent surface.
Ex :- solid paper , frosted glass
Reflection of light :-
When ray of light incidence on an opaque surface then the surface bounce back the ray of light in the same medium, this phenomena of light is known as reflection of Light

The ray of light which falls on the plane surface is called incident ray
The ray of light which is sent back by the plane surface is reflected rays
The perpendicular which is drawn on the surface is called normal.
The point at which the incident ray fall on the surface is called point of incidence.
There are two laws of reflection:
1st laws :- According to first law of reflection of light angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
“i” is the angle of incidence
“r” is the angle of reflection
∠i = ∠r

2nd laws :- According to second law of reflection of light Incident ray, reflected ray & normal lie in the same plane at same point of incident.
Note :- If the light ray falls normally or perpendicular on the surface then it will be reflected back along the same path.
∠i = ∠r = 0
Types of Reflection
(1) Regular Reflection:
When ray of light incident on smooth or polished surface then regular reflection takes place.
All reflected rays will be parallel to each other if incident rays are parallelly incident on the surface.
Intensity of image will be as usual.
Single intensified image is formed.

1. Irregular Reflection
When ray of light incident on rough surface then irregular reflection takes place.
• All reflected rays will not be parallel to each other if incident rays are parallelly incident on the surface.
• Intensity of image will be dull.
• More than one image is formed.

Reflection on Plane Surface
Plane Mirror: It is a reflecting object whose one face is reflecting and another face is polished.

IMAGE
When two or more reflected rays either meet or appear to meet, then image is formed.
There are two types of images:
Real Image
Virtual Image
Real Image
Real image is when two or more reflected rays actually meet after reflection, then real image is formed.
Real image can be obtained on the screen and it can be touched. Real image can be formed by concave mirror and convex lens.
(2) Virtual Image (Imaginary)
When two or more reflected rays appear to meet after reflection, then virtual image is formed.
Examples
(i) Plane mirror
(ii) Convex lens
(iii) Concave lens
(iv) Concave mirror
(v) Convex mirror
Image Formation in a Plane Mirror
- Image formed by mirror is virtual and erect.
In plane mirror, the distance of object in front of the mirror () is always equal to distance of image formed by the mirror ():
In plane mirror, height of object is equal to height of image. HO=HI
In plane mirror, left part of object appears right and right part of object appears left.
This phenomenon in plane mirror is called lateral inversion.

Multiple Reflection in plane Mirror
When two plane mirrors are inclined at angle θ then more reflection on the surface.
This phenomena is known as multiple Reflection
It causes formation of more then one image

1) If N is odd, then no. of image = N
Here L₁ L₂ & L₃ are image formed by plane mirror.

Note:-
• Focus of plane mirror is at infinite.
• Focal length of plane mirror is infinite.
• Magnification of plane mirror is 1.
• Power of plane mirror is 0.
Uses of plane mirror
- Face mirror:- Plane mirrors are used to see our face
- Solar cooker
- The plane mirror are fitted on the inside wall of certain shops to make them look bigger.
- Plane mirrors are used in making Periscope
Reflection on the Curve Surface
Spherical mirror:
Spherical mirror are those whose reflecting surface is curved inward or outward.
Reflecting Surface of spherical mirror is a part of hollow sphere of glass.
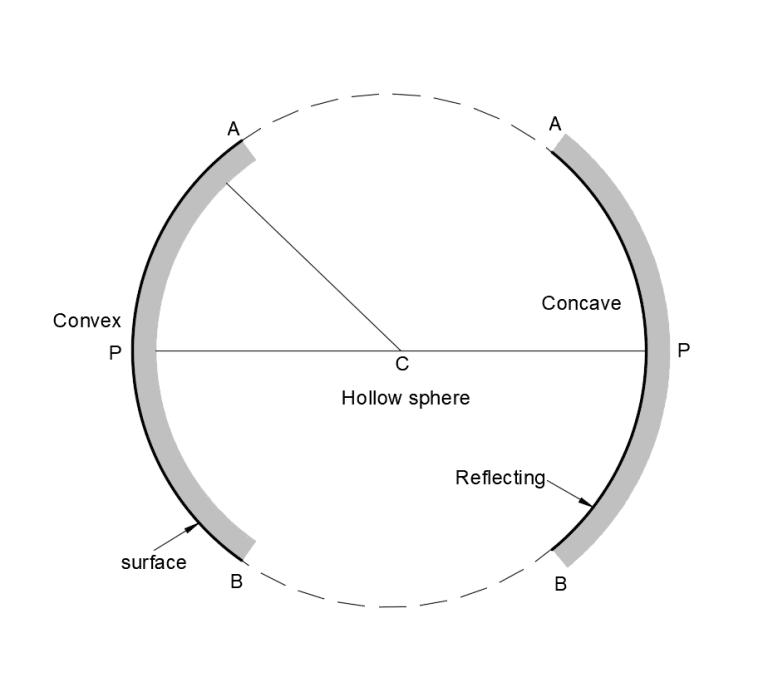
Hollow Spherical (Spherical mirror)
There are two types of spherical mirror:
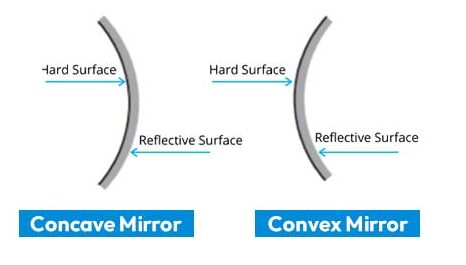
- Concave mirror
- Convex mirror
1) Concave mirror –
It is a part of spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is inward the center and polished surface is outward.
• It is also known as converging mirror.
• It has real focus.
• It form
(i) Real & inverted
(ii) Virtual & erect images.
• It’s focal length is negative.
• It form both
(i) Enlarged
(ii) Same the size of object
Concave mirror
2) Convex Mirror –
It is a part of spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is outward the center and polished surface is inward.
• It is also known as diverging mirror.
• It has virtual focus.
• Its focal length is positive.
• It always form virtual and erect image.
• Convex mirror has long range of view.
• It always form diminished image.
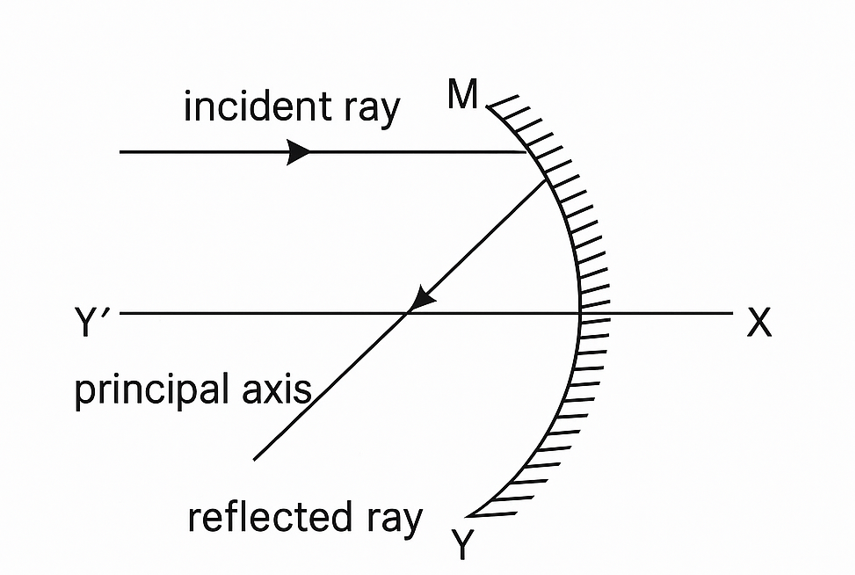
Q. Why concave mirror is called converging mirror?
In concave mirror if a ray parallel to principal axis incident on the reflecting surface then after reflection it will turn towards the principal axis and so concave mirror is called converging mirror.
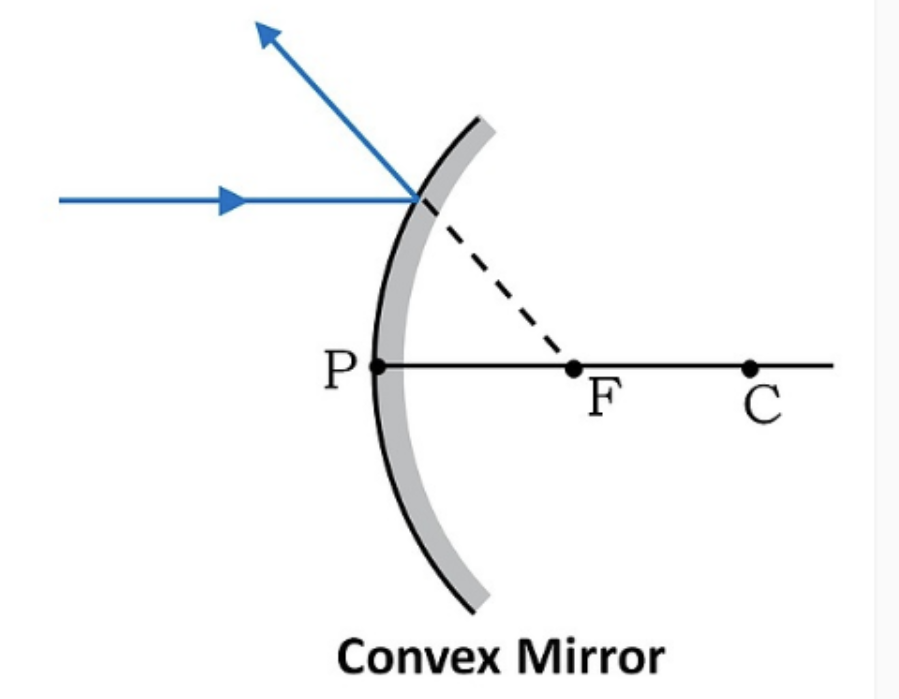
Que. – Why convex mirror is called diverging mirror?
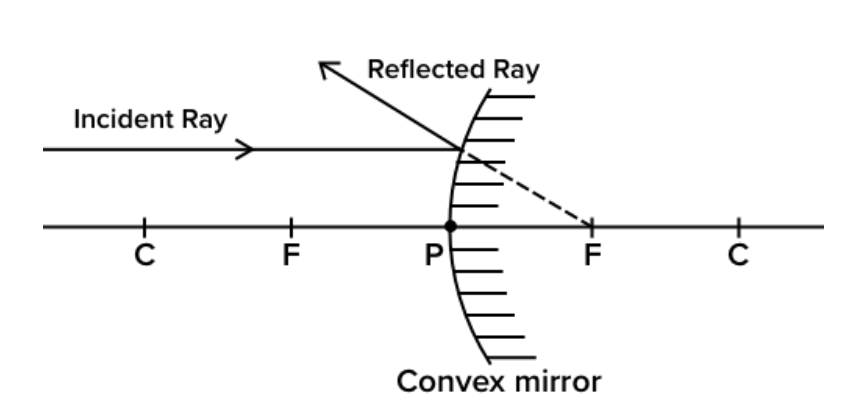
=> In convex mirror if a ray parallel to principal axis incident on the reflecting surface of mirror then after reflecting it will turn away from the principal axis so convex mirror is called diverging mirror.
Terms Related to Spherical Mirror
i) Principal Axis :- The line joining the center of curvature and pole is called principal axis.
ii) Pole (P): It is the mid-point of mirror or it is the center of the reflecting surface of concave or convex mirror.
=> Principal axis passes through it.
iii) Centre of Curvature (C): It is the Centre of hollow sphere whose one of the parts of spherical mirrors, (Concave / Convex)
=> It is denoted by C
iv) Radius of Curvature (R): It is the distance between pole and center of curvature.
=> It is denoted by R
v) Focus (F): It is the point on the principal axis where reflected rays either intersect or appears to intersect it when rays incident on the reflecting surface of mirrors parallel to principal axis.
=> It is denoted by F.
1. Concave Mirror has real focus.
2. Convex Mirror has Virtual focus.
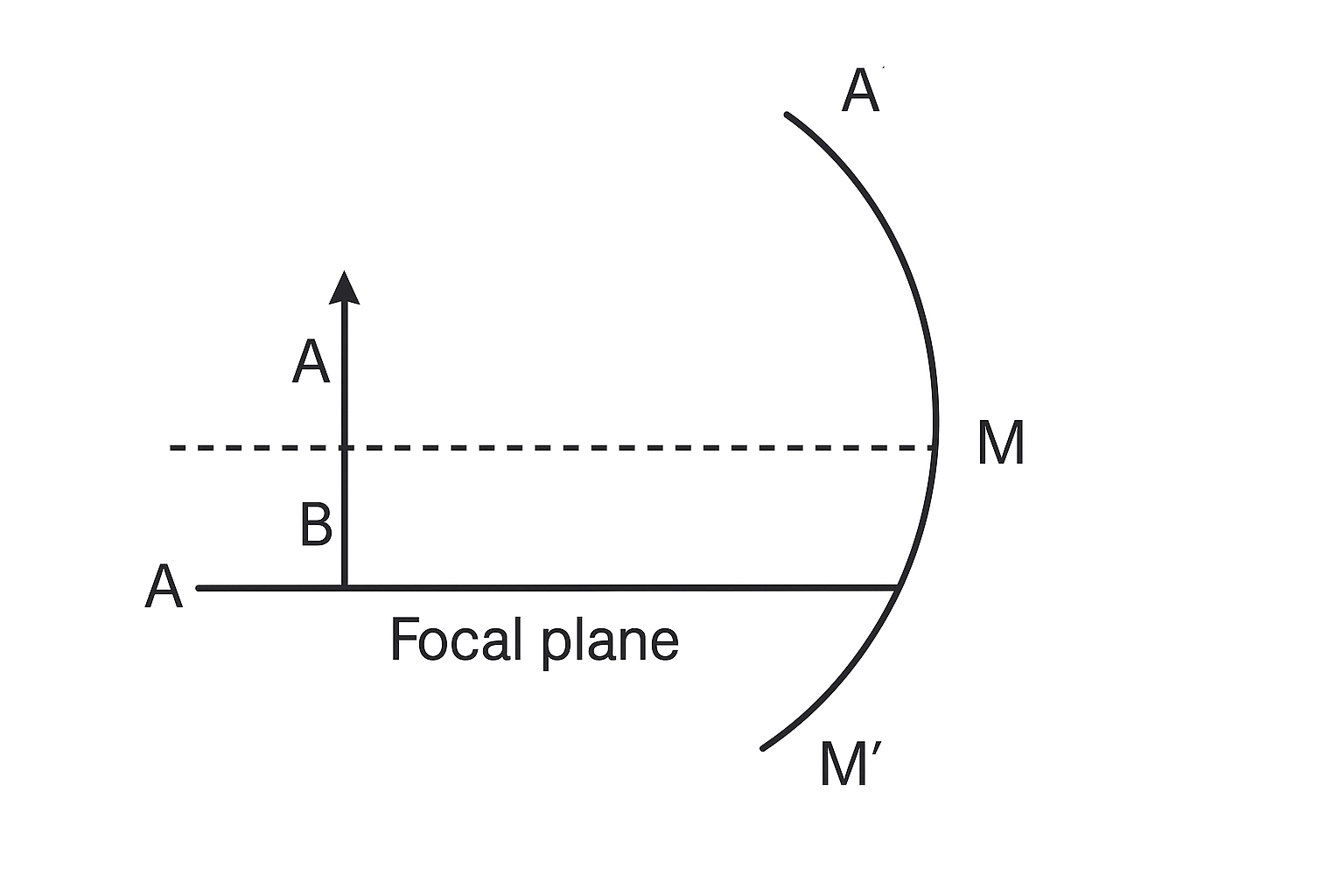
vi) Focal Length (f ) :- It is the distance between focus and pole
=> It is denoted by f.
=> Focal length of Concave mirror is Negative.
=> Focal length of convex mirror is Positive.
vii) Object distance (o): It is the distance between object and pole.
=> It is denoted by o.
=> Object always kept left side reflecting surface of mirror.
=> Object distance is always Negative.
viii) Image distance (v): It is the distance between pole and image formed.
=> It is denoted by v.
=> Real image formed towards reflecting face of mirror (in front of mirror).
=> Real image of mirror is always Negative.
=> Virtual image formed towards polished face of mirror (behind the mirror).
=> Virtual image of mirror is always Positive.
ix) Focal plane: A plane drawn perpendicular to focus of spherical mirrors (Convex / Concave) is called focal plane.
x) Centre of aperture :-
The effective diameter of the circular outer line of reflecting surface of spherical mirror is called aperture.
The lens whose aperture is much lesser than its radius of curvature is known as reflecting surface with small aperture.
Relation between focal length and radius of curvature of a Mirror
In a spherical mirror (concave/convex) focal length is equal to half of radius of curvature
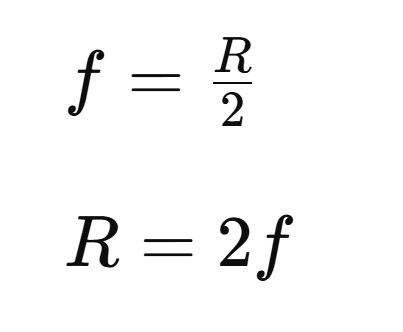
And the radius of curvature of spherical mirror is twice the focal length of the mirror.
• focal length of concave mirror = -ve
• focal length of convex mirror = +ve
• Radius of curvature of concave mirror = -ve
• Radius of curvature of convex mirror = +ve
Rules for making ray diagram by concave mirror
1st rule: A ray parallel to principal axis will pass through focus after reflection.
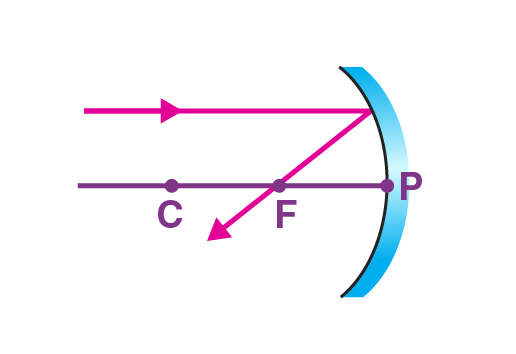
2nd rule: A ray passing through focus of concave mirror will be Parallel to principal axis after reflection
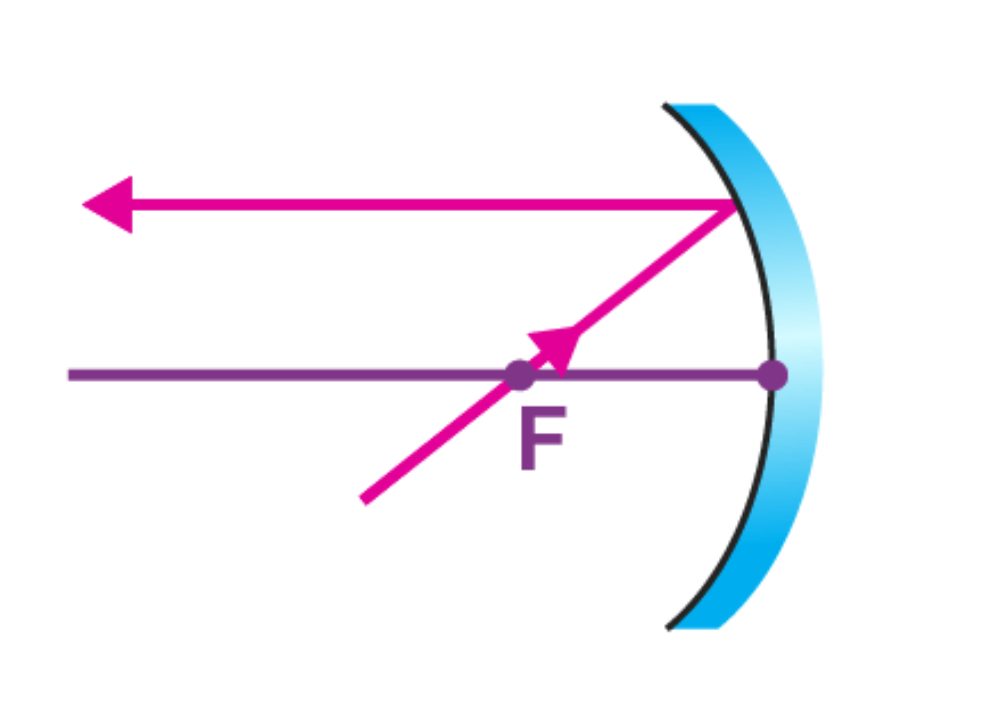
3rd rule: A ray of light passing through Centre of Curvature of Concave mirror will be reflected back on the same path after reflection.
Line joining Centre of curvature to the any point the surface of mirror is the normal to the point.
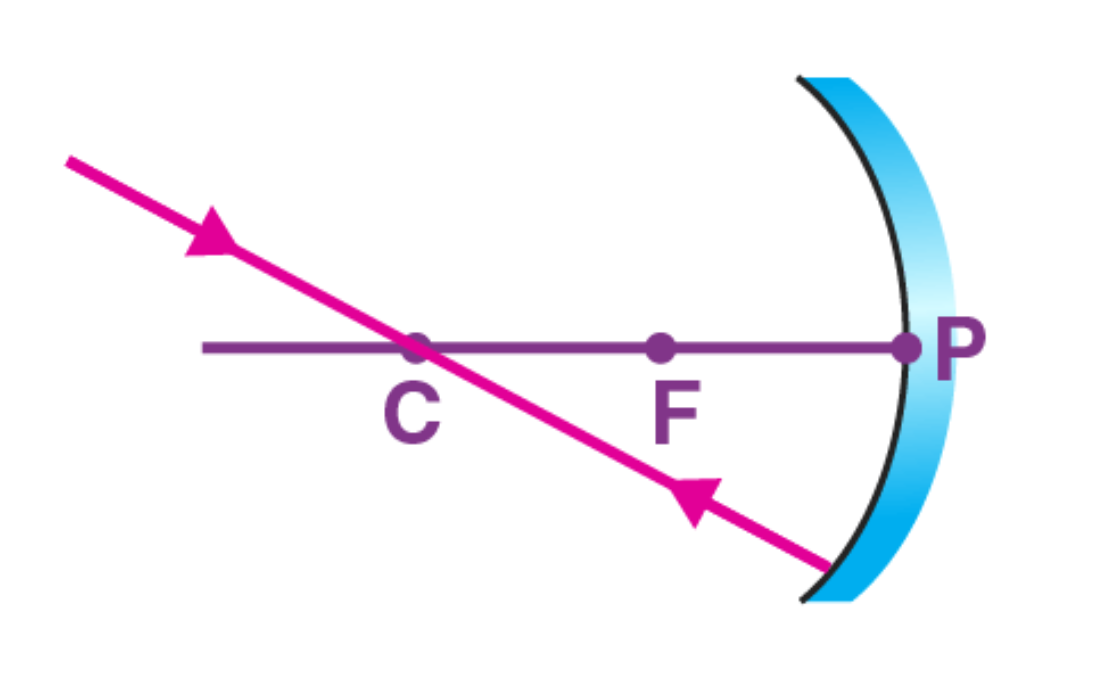
4th rule: A ray light which incident at the pole of concave mirror is reflected back making the same angle with the principal axis.
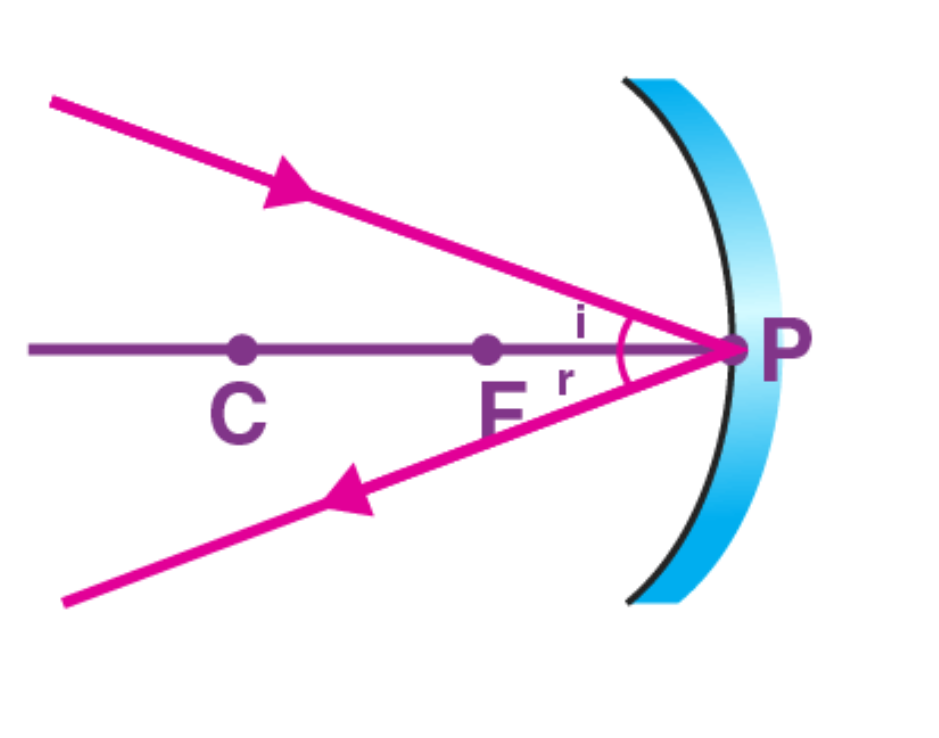
Image Formation In Concave Mirror
There are six ways to form images in concave mirror.
• Concave mirror form both real & virtual images.
• Concave mirror form diminished, enlarged and same size of images.
1️⃣ At infinity
2️⃣ Beyond the Center of curvature
3️⃣ At the Center of curvature
4️⃣ Between focus (F) & center of curvature (C)
5️⃣ At the focus (F)
6️⃣ Between pole (P) & focus (F)
1️⃣ When Object is kept at infinity then its real inverted and highly diminished image id formed at focal.
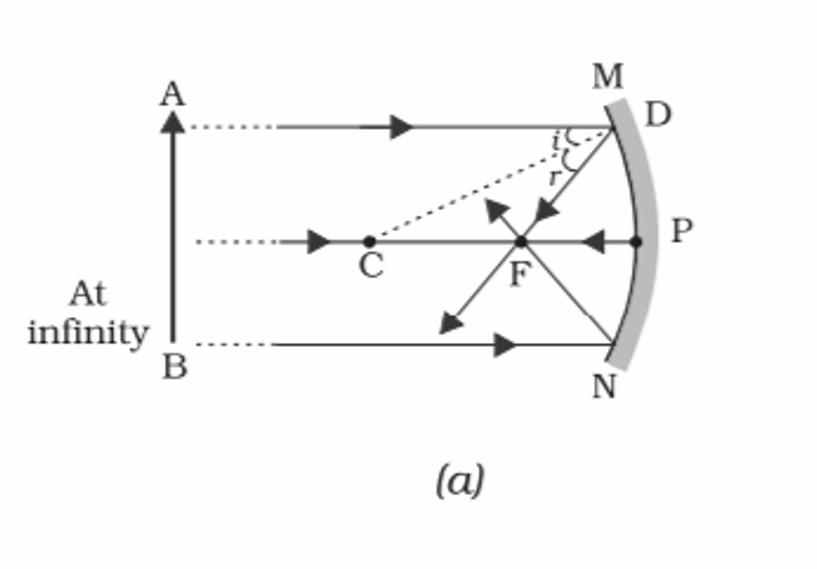
Conclusion:-
Position of Object- At Infinity
Position of Image- At focus
Size of Image- Highly diminished
Nature of Image- Real and Inverted
2️⃣ When object is placed beyond Center of curvature.
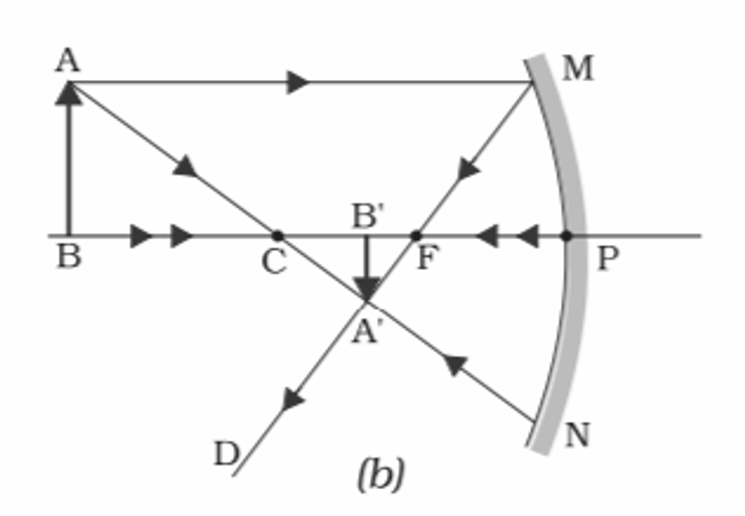
Conclusion:-
Position of Object- Beyond center of curvature
Position of Image- Between center of curvature and Focus
Size of Image- Diminished or Smaller than object
Nature of Image- Real and Inverted
3️⃣ When object is kept at Center of Curvature
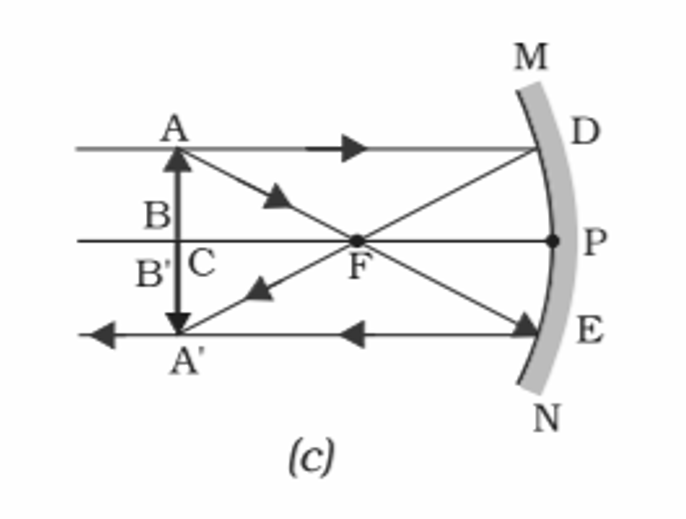
Conclusion:-
Position of Object- At Center of Curvature
Position of Image- At Center of Curvature
Size of Image- Same size as object
Nature of Image- Real and Inverted
4️⃣ When object is placed between center of curvature and focus
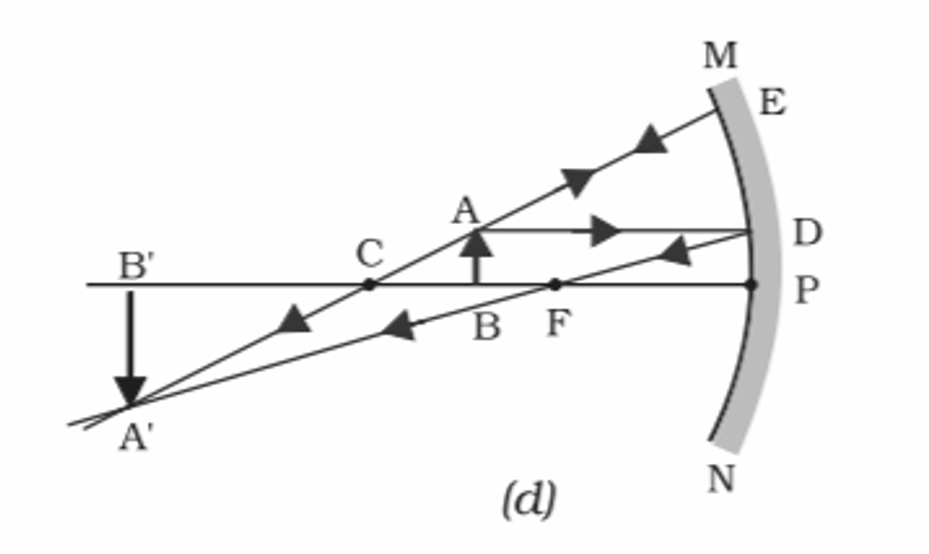
Conclusion:-
Position of Object- Between center of curvature and focus
Position of Image- Beyond Center of Curvature
Size of Image- Larger than the object
Nature of Image- Real and Inverted
5️⃣ When an object is placed at focus
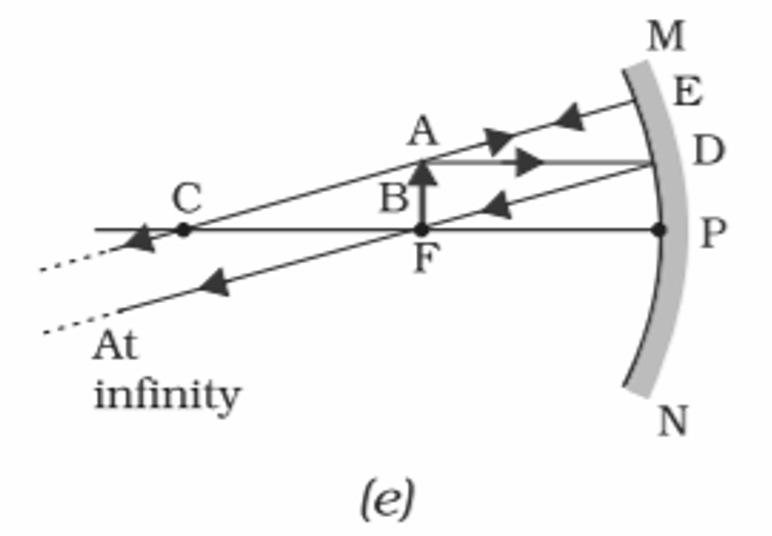
Conclusion:-
Position of Object- At Focus
Position of Image- At Infinity
Size of Image- Highly Magnified
Nature of Image- Real and Inverted
• As we know that infinity doesn’t exist so image will be distance when object is kept at focus.
6️⃣ When object is placed between focus and pole
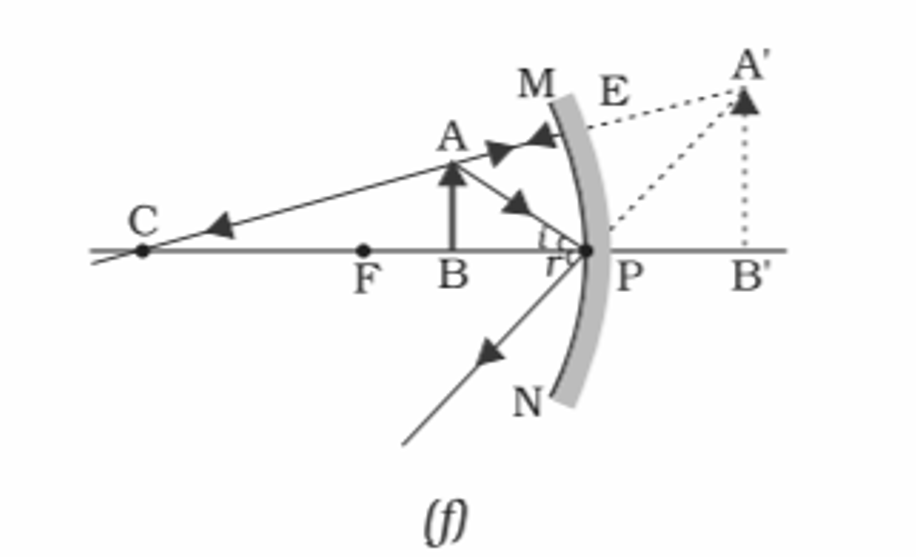
Conclusion:-
Position of Object- Between Focus and pole
Position of Image- Behind the Mirror
Size of Image- Larger than the Object
Nature of Image- Virtual and Erect
Uses Of Concave Mirror :-
i) It is used as shaving mirror to see the large image of face and it is also used for a makeup mirrors
ii) It is used by Dentist to see the large image of the of the patient.
iii) It is used by reflectors in torch vehicle’s headlights to get powerful beam of light.
iv) It is used as doctor’s head mirrors to focus the light coming from the lamp on the body part of the patient such as eye, ear, nose etc.
v) Concave dish are used in TV dish antenna to receive TV signals from the distant communication satellites.
vi) Large Concave mirrors are used in the field of solar energy to focus Sun’s rays for heating solar furnace.
Rules for image formation in Convex Mirror
1st rules :- When a ray of light parallel to principal axis, incident on the surface of mirror then after reflection the diverge reflection rays appears to pass from focus.
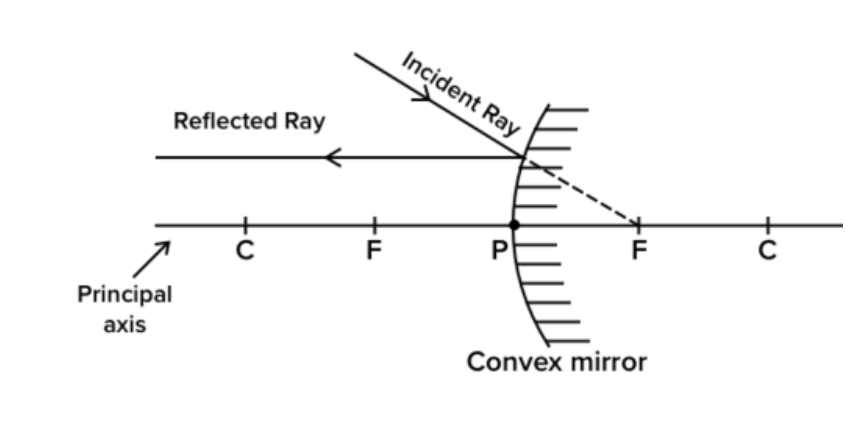
2nd rules :- A ray of light appears to passes from focus in a convex mirror. It will parallel to principal.
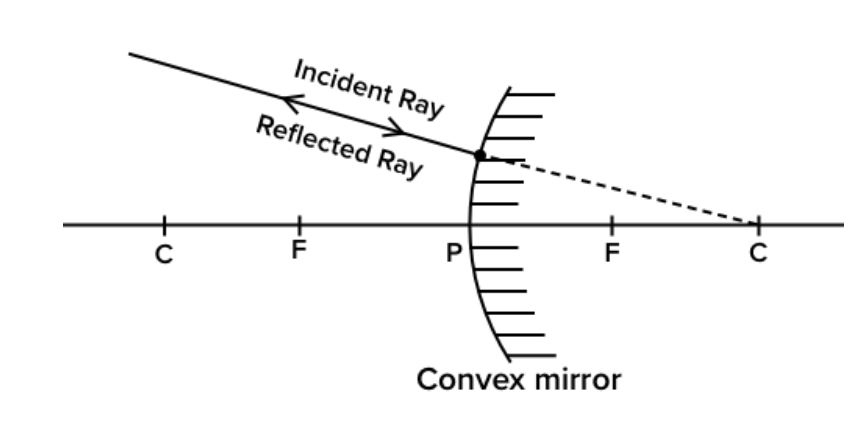
3rd rules :- When a ray of light appears to pass from center of curvature then after reflection it will be bounce back on the same path.
4th rule :- When a ray of light incident at any point on the reflecting surface, then it will follow the laws of reflection.
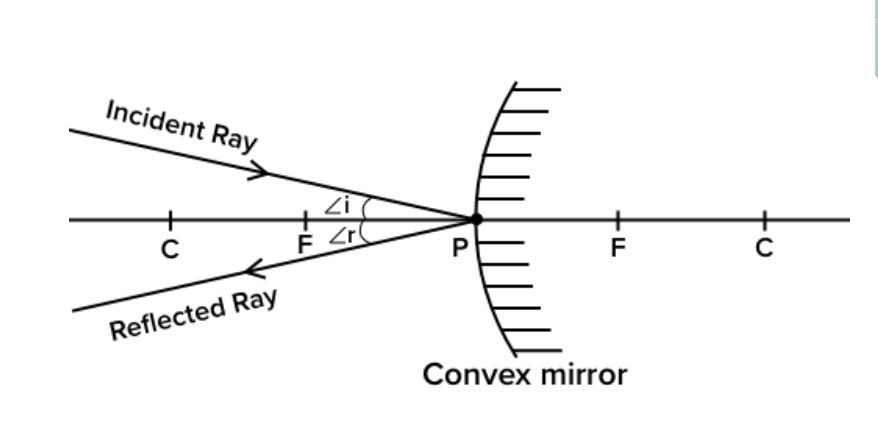
Image Formation In Concave Mirror
There are six ways to form images in concave mirror.
1️⃣ When object is kept at infinity
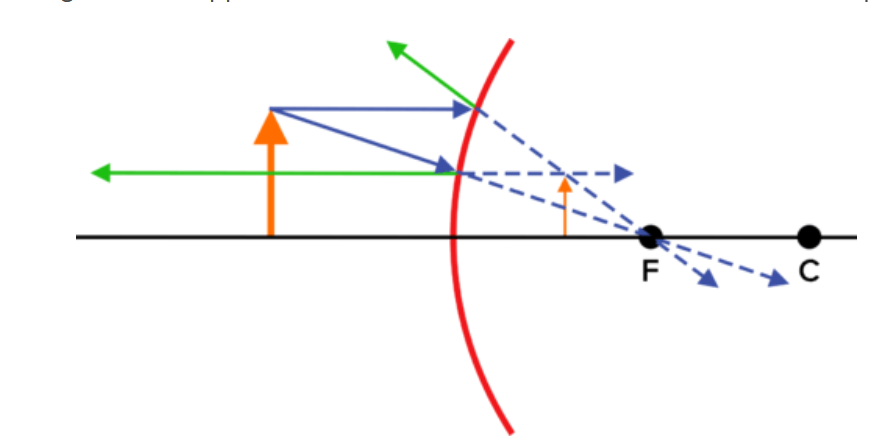
Conclusion:-
Position of Object- At Infinity
Position of Image- Behind the Mirror
Size of Image- Highly Diminished
Nature of Image- Virtual and Erect
2️⃣ When object is placed between Pole and Infinity
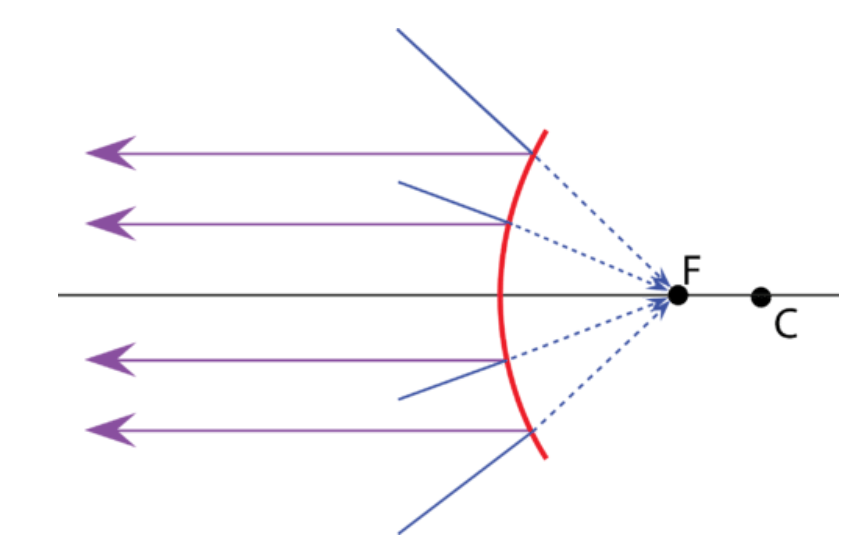
Conclusion:-
Position of Object- Between pole and Infinity
Position of Image- Between pole and focus
Size of Image- Diminished
Nature of Image- Virtual and Erect
Uses Of Convex Mirror :-
- Convex mirrors are used as rear (back) mirrors of cars, bike.
- Convex mirrors are used as road turns.
- Big convex mirror are used as shop security mirror.
- Whenever we need to see large object like buildings or frames.
Sign Convention of Spherical Mirror
Object and reflecting surface shout be at left,
Pole will be the origin
All the distance along principal axis will be measured from pole.
Along PX distance will be measured positive.
Along PX’ distance distance will be measured negative.
Along principal axis we measured distance of object from pole, which is denoted by (u) and sign will be negative.
Distance of image will be measured from pole which is denoted by (v)
Height of object will be measured above principal axis (positive) denoted by H.
Height of image will be measured above or below the principal axis and measured from pole.
Mirror formula
➔ It expresses the relationship among image distance, object distance & focal length such that reciprocal of focal length is equal to sum of reciprocal of image distance and object distance.
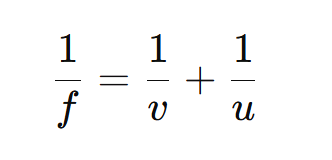
Magnification
➔ It states that an image is how many times that of an object.
➔ It is the ratio of image distance and object distance.
➔ It is the ratio of height of image to height of object.
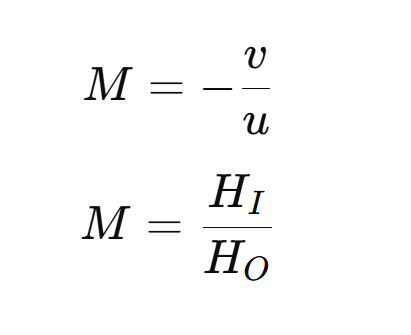
➔ It has no unit
M = +ve
That image is virtual and erect.
If M<1M < 1
→ Convex mirror
M = -ve
That image is real & inverted
If M>1→ Concave mirror
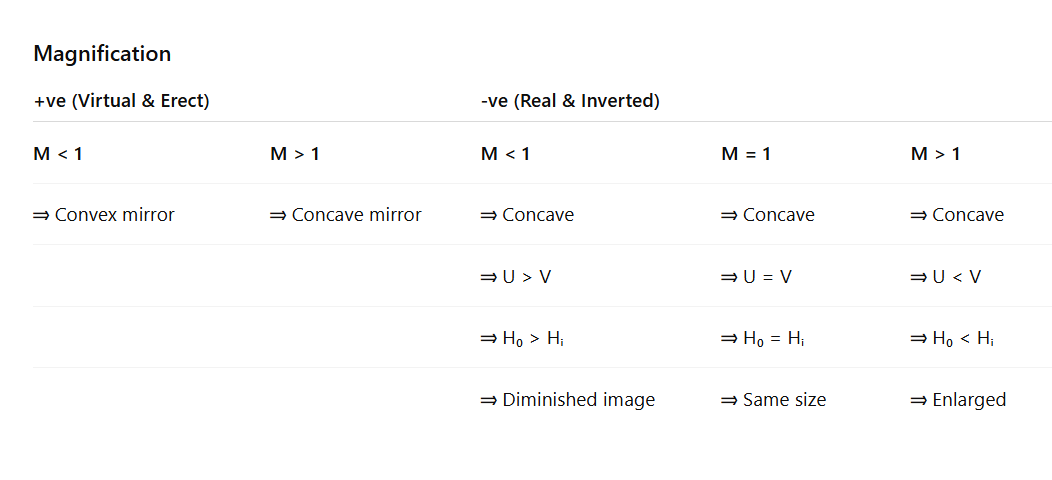
Red & inverted
virtual image enlarged = Concave
virtual image diminished = Convex
Home – View
Official Website- Physics Wallah
iOTA CLASSES has been working for the last 6 years at youtube ( online mode) but from last year ( 2024) we are running both online and offline,
With the cooperation of students , parents , our colleagues and team, we have gained satisfactory results,
And working more enthusiastically for the better aspirations. image of 2024 class 10th result [CBSE and BSEB( ENG. Med)]