Units and Measurement Class 9
⇰ Measurement in every day life
Example –
- Measurement of mass.
- Measurement of volume.
- Measurement of length.
- Measurement of temperature.
⇰ Definition of measurement
→ Measurement is the process of associating numbers with physical quantity and phenomena.
→ Measurement is fundamental to the science to engineering, construction, and other technical field and to almost all everyday activities.
⇰ Need of measurement in Physics
- To understand any phenomenon in Physics we have to perform experiments.
→ Experiment require measurements and we measure several physical properties like length, mass, time, temperature, pressure, etc.
→ Experimental verification of laws and theories also needs measurement of physical properties.
Physical Quantity →
A physical property that can measured and describe by a number is called physical quantity.
Example →
- Mass of a person is 60 kg.
- Length of a table is 3 m.
- Area of a hall is 100 m².
- Temperature of a room is 300°K.
Types of Physical quantity
- Fundamental quantities
- Derived quantities
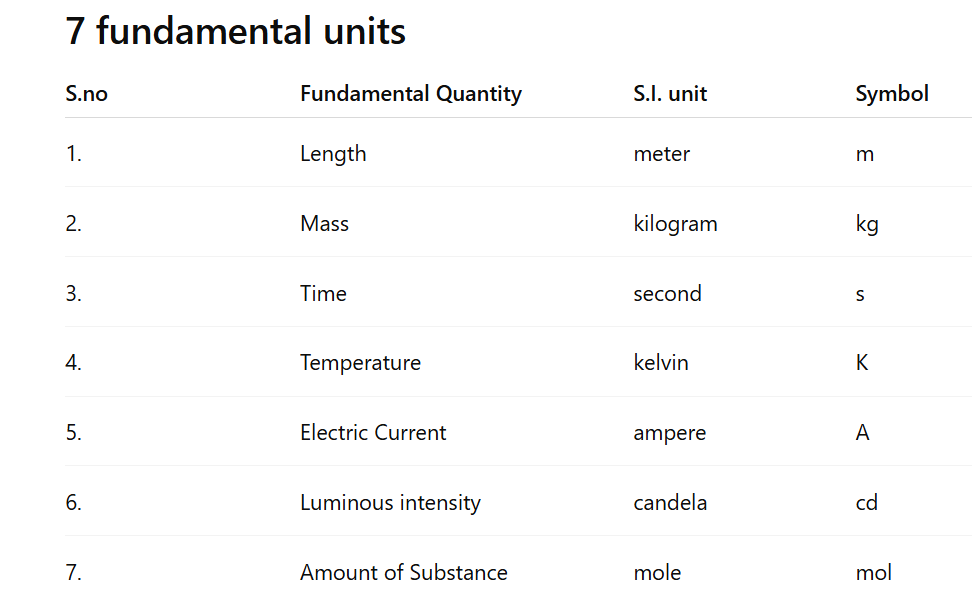
i) The physical quantity which do not depend on any other physical quantity for their measurements is known as fundamental quantities.
Example →
Mass, Length, Temperature, Luminous intensity, Time, Ampere, Mole.
ii) The physical quantity which depends on one or more fundamental quantities for their measurements is known as derived quantities.
Example →
Area, Pressure, speed, volume, force, etc.
⇰ Unit for measurement
→ The standard used for the measurement of a physical quantity is called a unit.
For example →
Meter, Foot, Inch for length.
Kilogram, Pound for mass.
Second, minute, hours for time.
Fahrenheit, Kelvin, Celsius for Temperature.
⇰ Characteristics for unit
- Well define
- Suitable size
- Invariable
- Internationally acceptable
⇰ Types of physical quantity on the basis of magnitude and direction
(i) Scalar Quantity
(ii) Vector Quantity
(i) Scalar Quantity
A physical quantity which has only its magnitude is known as Scalar Quantity.
Example –
Distance, time, power, pressure, energy, speed, volume, area, density, work, temperature, charge, electric current, frequency, mass, etc.
(ii) Vector Quantity
A physical quantity which has both magnitude as well as direction is known as vector quantity.
Example →
Displacement, velocity, acceleration, force, weight, momentum, magnetic field, elastic field etc.
Types of Unit
- C.G.S. System
- M.K.S. System
- F.P.S. System
- International System of unit (S.I. unit)
i) C.G.S. System
• This system was first introduced in France
• It is also known as gaussian system of units.
• It based on Centimeter, gram and second as the Fundamental units of length, mass and time.
ii) M.K.S. System
• This system was also introduced in France.
• It is also known as French system of units.
• It is based on Meter, Kilogram and Second as the Fundamental units of length, mass and time.
iii) F.P.S. System
• This system was first introduced in Britain.
• It is also known as British System of units.
• It is based on Foot, Pound and Second as the Fundamental units of length, mass and time.
iv) S.I. unit
• In 1971 general conference on weight and measures hold its meeting and decided a system of unit for international uses.
• This system is called International system of units and abbreviated as S.I. from its French name.
Home – View
Official Website- Physics Walla
iOTA CLASSES has been working for the last 6 years at youtube ( online mode) but from last year ( 2024) we are running both online and offline,
With the cooperation of students , parents , our colleagues and team, we have gained satisfactory results,
And working more enthusiastically for the better aspirations. image of 2024 class 10th result [CBSE and BSEB( ENG. Med)]




